TEF Braids and Tensengral have developed an evolutionary form of manufacturing and design based upon the fundamental concept of braided lace technology, resulting in a revolutionary technology that can be used for zero-waste, performance driven production across a spectrum of uses.
-
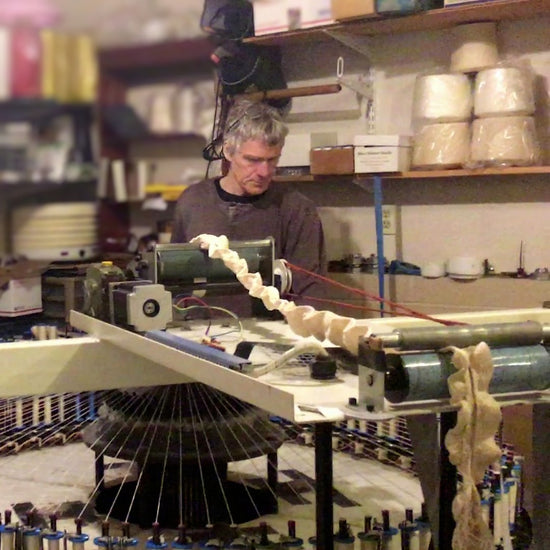

What is your sustainable innovation?
We’ve developed a multi-faceted approach to sustainability through design, material and manufacturing innovations.
-
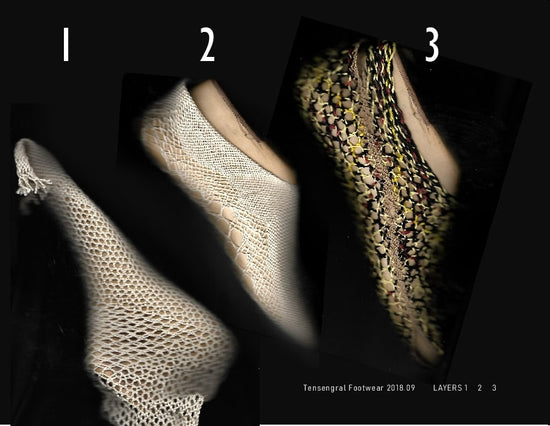

Design Innovation
We’ve created a new way of designing products from linked and interlaced filament networks. This new way of making things uses a minimum of materials which is important as resources become less abundant.
-
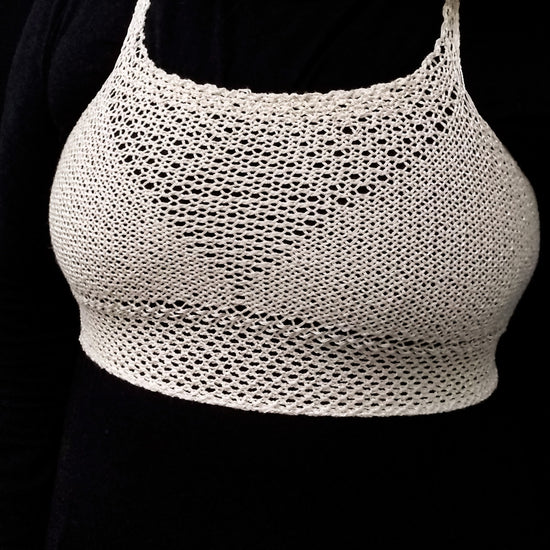

In our design process, the yarn is the product -- meaning, function is built into the product by the way the yarns that make up the fabric are organized.
-
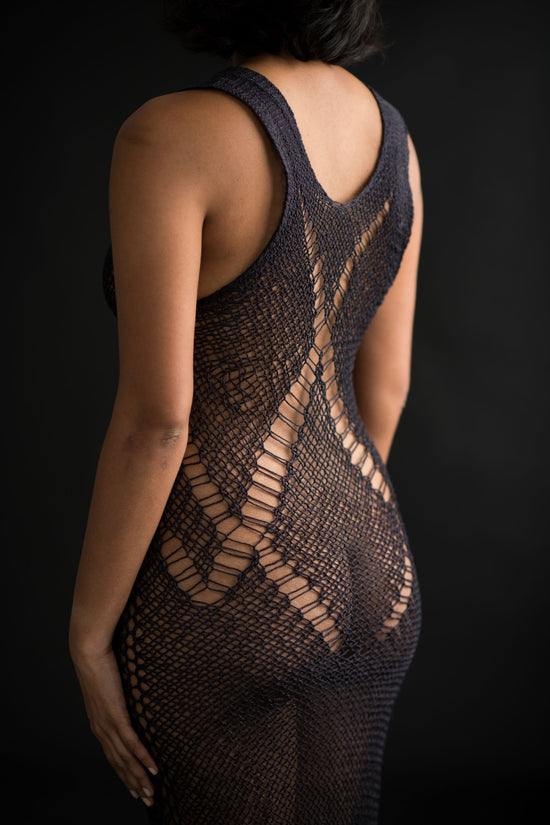

Material Innovation
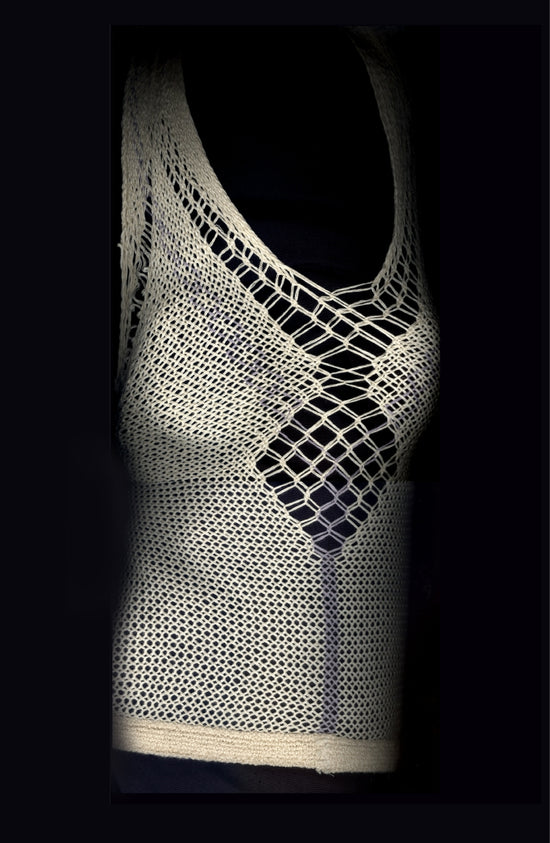
The fabric we've invented is made of yarns that are linked in a multitude of ways, creating an unbound, unified web-like material that has the capacity to conform to contours and shape-shift in response to movement.
-
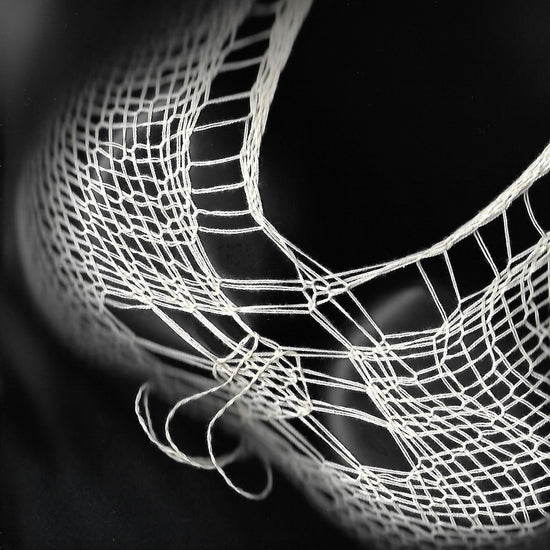

When on the body, the fabric provides a "fluid support", the result of filament networks subtly shifting to distribute the tensions caused by motion.
-
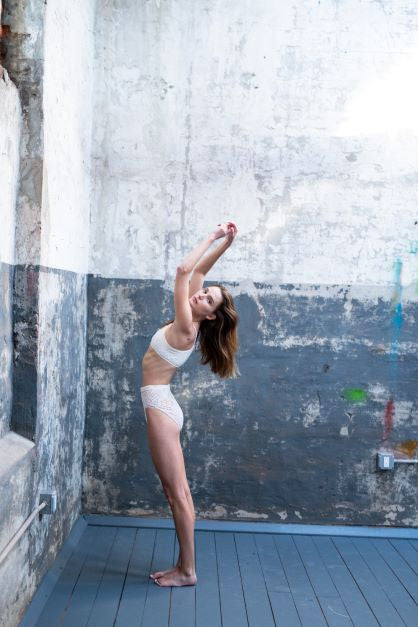

Such fluidity mimics the strategies of nature, providing a fabric that feels almost alive because it holds and stays with you as you move.
-
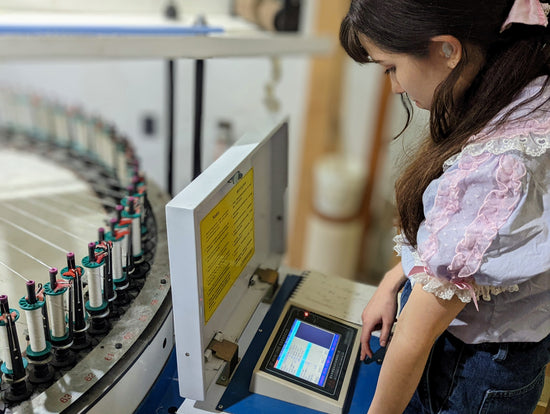

Manufacturing Innovation
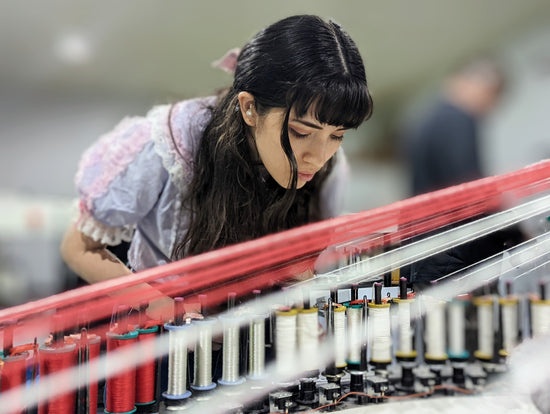
We've repurposed virtually unknown and under-appreciated circular lace braiding machines that have been updated with electronics and a computer aided design systems, to make the fabric.
-
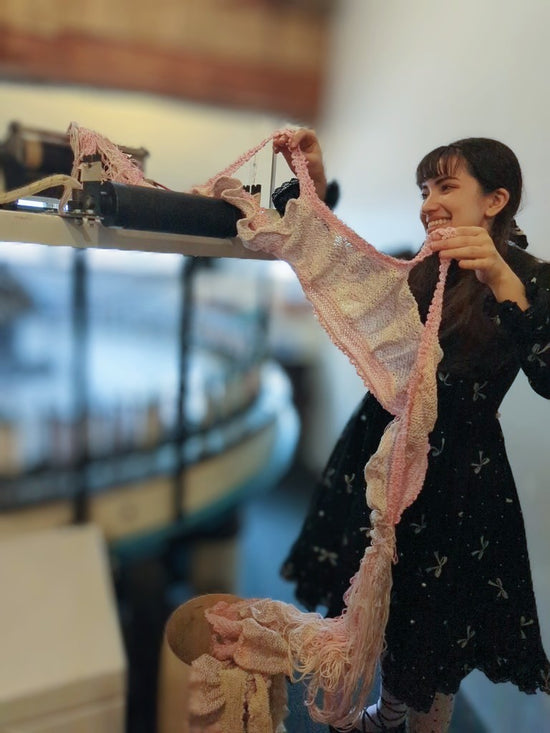

We produce the fabric for a product in one efficient virtually zero waste step, which is called additive or near-net manufacturing. This way of making things is the gold standard for sustainable production.
Our reimagined lace braiding technology can create zero-waste, performance driven textiles, structures, designs, and materials, with the potential to make planet positive impact across a broad spectrum of industries and professions.
-

Our manufacturing advancements and improvements to braided fabrics will enhance existing markets for braids that presently include aerospace, automotive, medical and sporting equipment industries, as well as create new ones where load distribution, fabric stability, zonal patterning and conformal qualities improve a products performance.
-
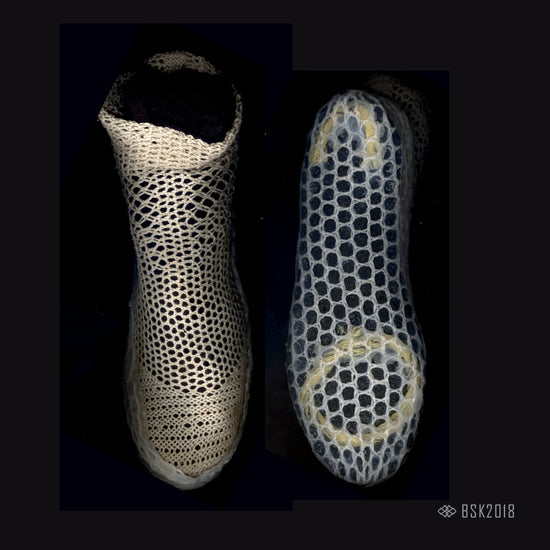
Braided fabrics, which are made from interlaced yarns, have historically been the reinforcement of choice in the engineering world when used in a composite structures. The use of braided fabrics in non-composite structures, as fabrics for textiles, has been overlooked.
-

Because the fibers within a braided structure are continuous, mechanically locked and able to evenly distributes load, braided fabrics provide strength and flexibility that is not characteristic of other woven fabrics.
-

We've redefined the scope of a braid by adding links in various combinations to the fabric's composition. The addition of links provides for a material with increased conform-ability and stability, while maintaining load distribution, strength and flexibility of traditional braided fabric.
-

The greatest value our brading process offers over existing ways of making braided fabric is the ability to zonally pattern the material so that different areas can provide different performance attributes.
-

This is only possible using a lace-braiding machine where the spindles can be programmed to move forward, back or not at all.
A step towards solving the excessive use and waste generated by multiple industries, while providing new perspectives to the performance and structure driven design challenges of today.
-
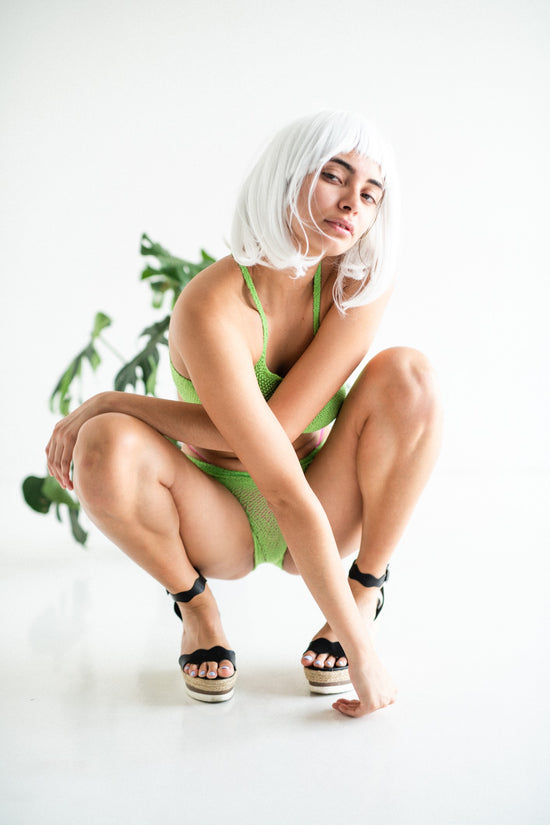

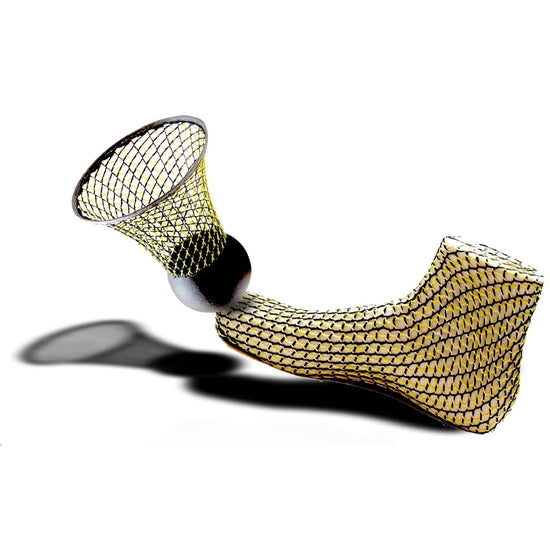
The linked and interlaced filament networks that our innovation utilizes provide endless possibilities for a variety of purposes.
-
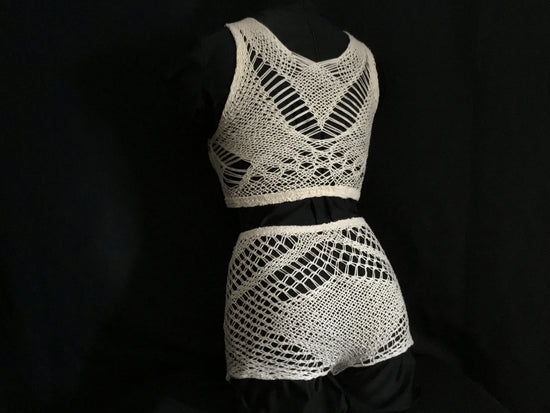

Aesthetically Driven with our array of patterns, we provide seemingly endless possibilities for creative and visually engaging designs.
-
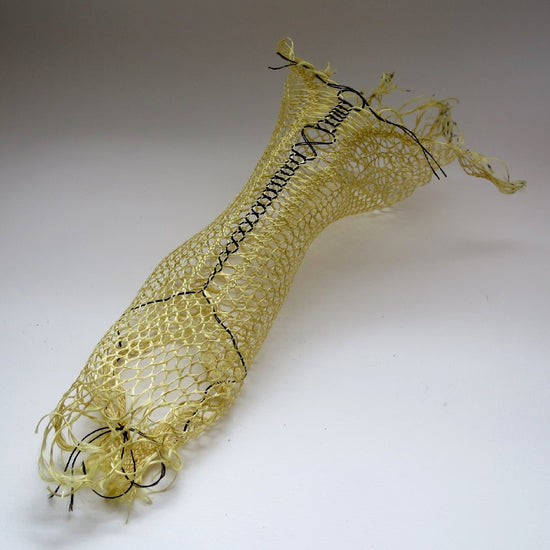

Performance Driven in purposefully patterning the tension and scale to manufacture, we have the capability to plan and design for a variety of practical uses across multiple industries.
-
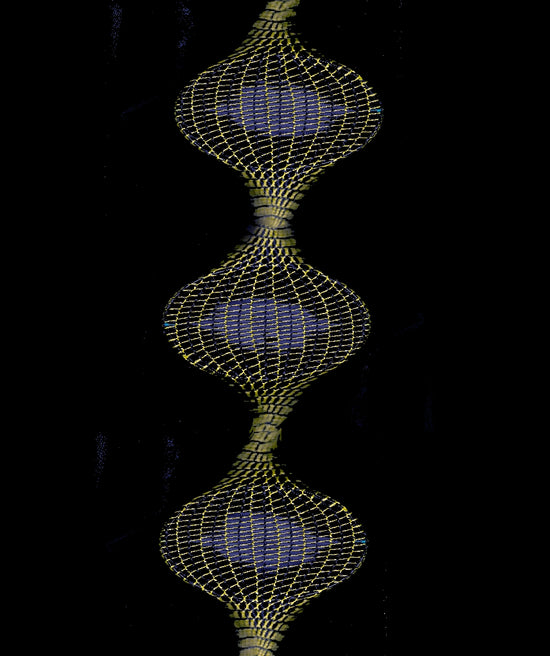
Experimental in end usage or the type of filament used, we meticulously blend utilitarian and artistic expression into new, exciting design driven possibilities for the future.
How far have you come in the development of your idea?
-
Amost two decades ago we began our self-education as to how to use a lace braiding machine to make fabrics other than lace.
-
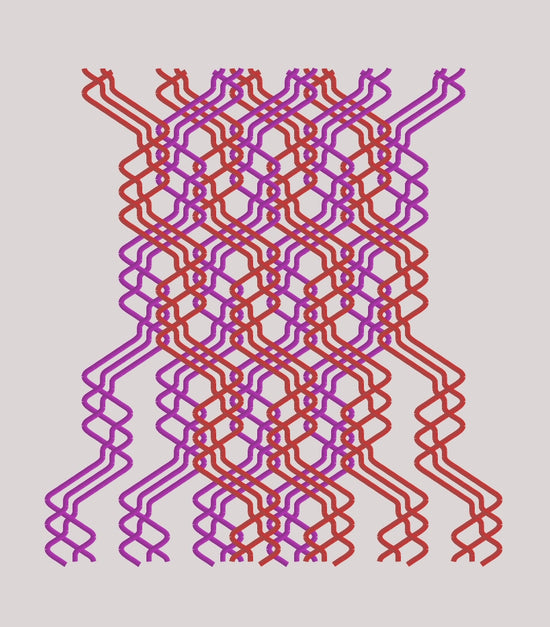
In order to make the technology work for us we designed a computer interface that would help us make new patterns for fabrics that would serve our purposes.
-
We patented these new patterns and use them to make products that merged the structural, distributive qualities of a braid with the fluid nature of a knit.
-

in 2021 we opened the only lace braiding manufacturing facility in the United State in order to scale the technology.
-
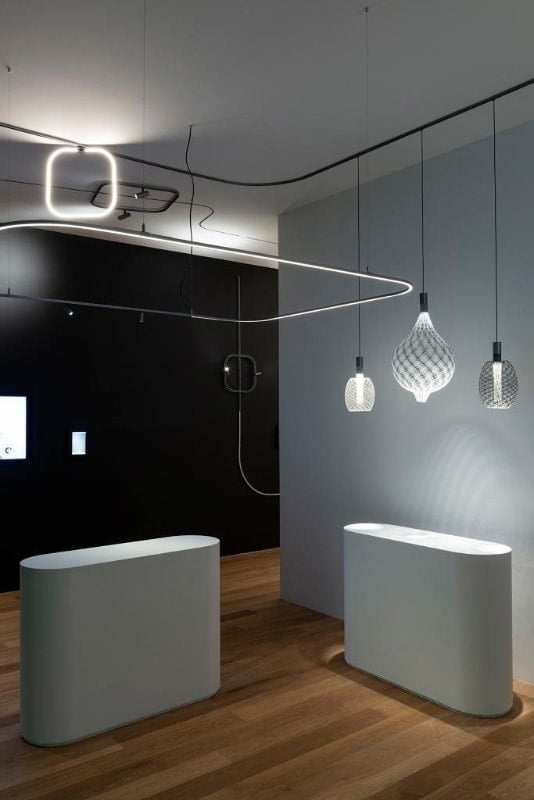

We've participated in brand and academic collaborations to explore the potential of our technology.
-
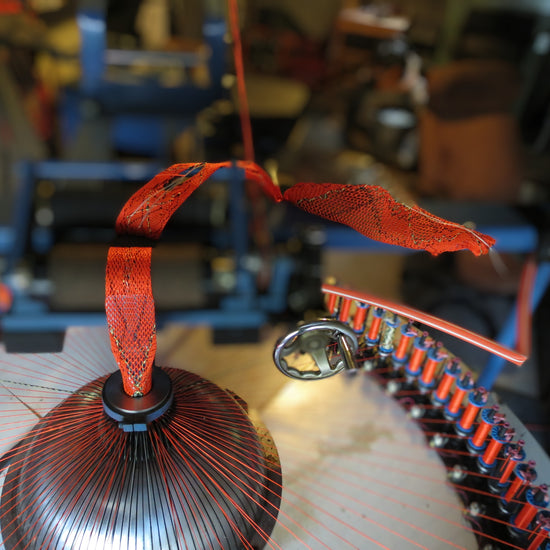

Our manufacturing advancements have provided new insights and product design options to markets such as apparel/footwear, biomedical/mechanical, electronics, lighting, automotive, aerospace, athletic, jewellery/accessories, construction/architecture.
The benefit of product creation using filament networks and zero waste, efficient manufacturing will inspire a new age of design that strives to use fewer resources in a more effective manner.
-
NEEDS: What important need do you want to solve?
The need for efficient, zero waste manufacturing systems that use fewer resources in a more effective manner, as well as reduction of excessive waste generated due to outdated design processes and performance expectations, for multiple industries, are the needs we address with our technology.
-
APPROACH: What is the solution? What or which technique do you think can solve the problem?
Our innovation in textile/design development builds upon the repurposing of lace braiding machines to create filament structures that can be zonally patterned, visually compelling, zero-waste products, using as few raw materials as possible in their construction while solving performance challenges.
-
BENEFIT: What is the benefit to the customer and stakeholders?
For the Consumer:
Comfort, Reduced Waste, Increased Performance,
Longevity, BeautyFor the Stakeholder:
Manufacturing Efficiency, Reduced Resource Consumption, Market Exclusivity
-
COMPETITION: Who are your main competitors and how do you differentiate from these?
For climate impact and waste reduction our efficient, zero waste manufacturing systems using designs that provide new performance expectations while using fewer resources, are the solutions we offer as alternatives to address the limitations of traditional braid, composite, knit, and woven structures currently on the market.

























